Division Calculator When You Know the Answer
Enter the divisor and dividend beneath to calculate the quotient and residuum using long partition. The results and steps to solve information technology are shown below.
Outcome:
| Full Reply: | 18 R 3 |
|---|---|
| Caliber: | 18 |
| Remainder: | 3 |
Solution
Learn how we calculated this below
On this folio:
- Computer
- How to do Long Division with Remainders
- Parts of a Long Partitioning Trouble
- Steps to Calculate a Long Partitioning Problem
- How to get the Quotient and Residue as a Decimal
- References
How to do Long Partition with Remainders
Learning long division is a crucial milestone in learning essential math skills and a rite of passage to completing elementary school. It strikes fear in simple school students and parents alike.
A recent study constitute that the agreement of long division and fractions in elementary school is directly linked to the student'southward ability to acquire and sympathize algebra later in school.[ane]
Accept no fear!
Learning long division can be easy, and in simply a few easy steps, yous tin solve any long division problem. Follow forth as we break it down, but kickoff, we need to cover the anatomy of a long division problem.
Parts of a Long Division Problem
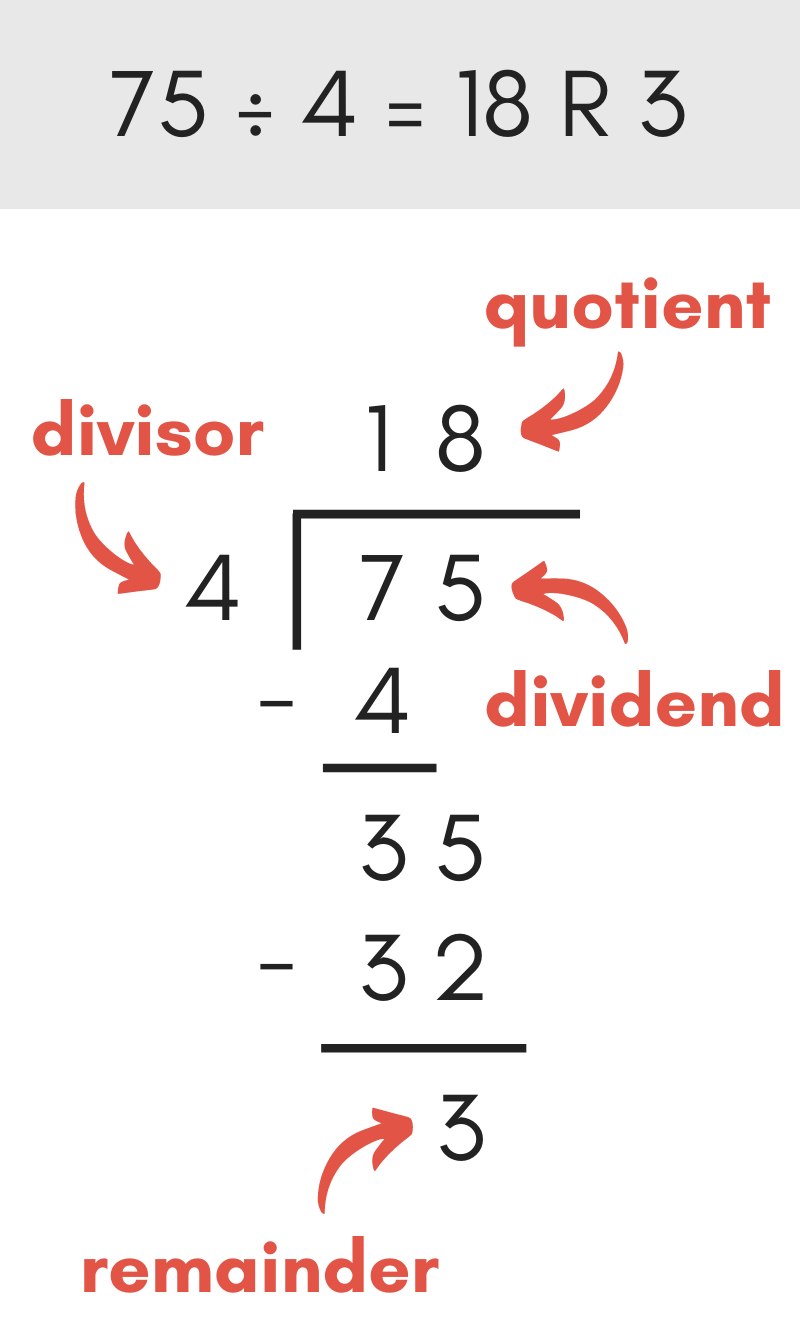
At that place are a few parts to a long division problem, as shown in the image above.
The dividend is the number to the right and under the division line and is the number being divided.
The divisor is the number to the left of the division line and is the number being dividing by.
The quotient is the solution and is shown above the dividend over the division line. Often in long division, the caliber is the whole number part of the solution.
The remainder is the remaining function of the solution, or what'southward leftover, that doesn't fit evenly into the caliber.
Steps to Calculate a Long Partitioning Problem
At that place are a few main steps to solving a long division trouble: divide, multiply, subtract, bringing the number downwards, and repeating the process.
Footstep 1: Set up the Equation
The showtime step in solving a long division problem is to draw the equation that needs to be solved. If the trouble is already in long division form, then skip along to step 2.
If information technology'south not, this is how to draw the long division trouble.
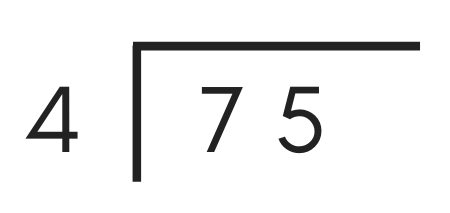
Start by drawing a vertical bar to split up the divisor and dividend and an overbar to split the dividend and quotient.
Place the dividend to the right of the vertical bar nether the overbar. Identify the divisor to the left of the vertical bar.
For example, to divide 75 past 4, the long partition problem should expect similar this:
Pace Two: Dissever
With the long segmentation trouble fatigued, start past dividing the commencement digit in the dividend past the divisor.
You tin can also think about this as counting the number of times the divisor volition fit into the digit in the dividend.
Drop the residue or decimal portion of the consequence and write the whole number portion of the consequence in the quotient above the overline directly to a higher place the digit in the dividend.
For example, the divisor "iv" goes into the first digit of the dividend "vii" i time, so a "1" can be added to the quotient.
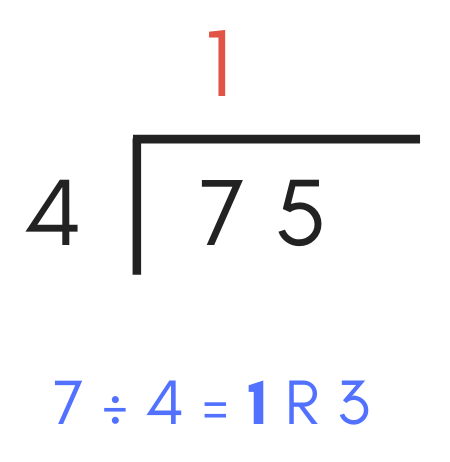
Step Three: Multiply
The next step is to multiply the divisor by the digit just added to the caliber. Write the result below the digit in the dividend.
This step forms the next part of the equation for the next step.
Multiplying the divisor "iv" by "1", which we institute in the previous stride, equals "four". So, add a "iv" below the offset digit in the dividend.
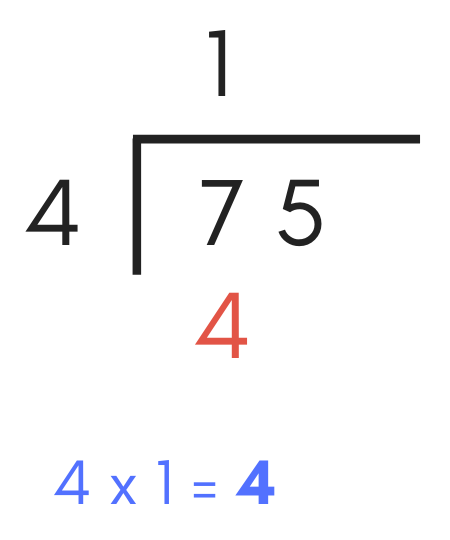
Stride Iv: Subtract
Now, add together a minus sign "-" earlier the number added in the previous step and draw a line below information technology to form a subtraction equation.
Continuing the example above, add a "-" before the "4" and a subtraction line below it.
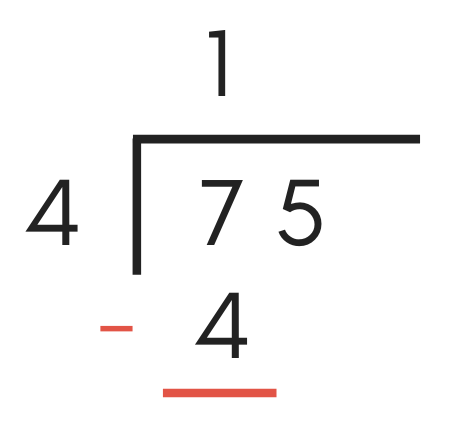
Now that you lot take a subtraction problem created, it'southward fourth dimension to solve it.
To solve, subtract "seven" minus "4", which equals "3", and so write a "3" in the equation.
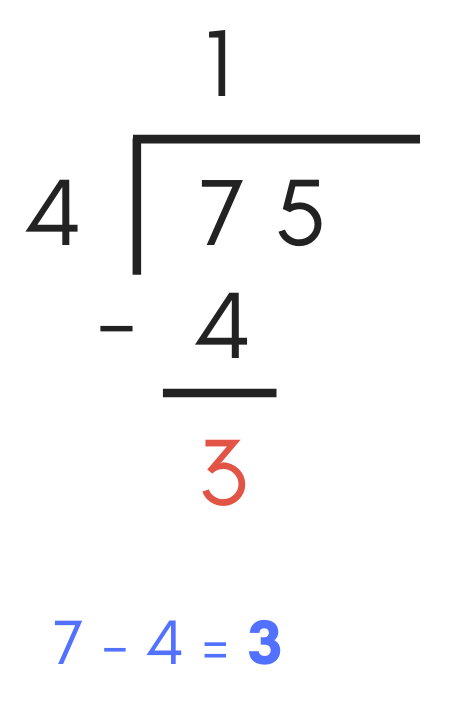
If the long division problem has a dividend that is a single digit, then hooray, you lot're done! The remaining number that is the outcome of the subtraction trouble is the remainder, and the number above the dividend is the solved quotient.
If more digits are remaining in the dividend, then proceed to the next step.
Pace 5: Pull Down the Next Number
At this point in the process, it's time to operate on the next number in the dividend. To do this, pull down the next digit in the dividend and place information technology direct to the right of the effect from the subtraction problem above.
The next digit in the dividend is "5". So, pull "5" downward and write it next to the "three" found in the previous step.
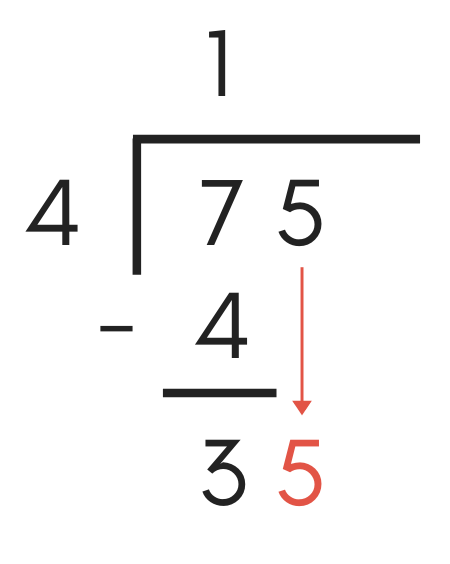
Step Six: Repeat
At this betoken, you might exist wondering where to go from here. Repeat steps two to five until all the digits in the dividend accept been pulled down, divided, multiplied, and subtracted.
When dividing, employ the result of the subtraction problem combined with the pulled down digit every bit the dividend and carve up the divisor into information technology.
Continuing the examples above, divide the result of the subtraction problem and the pulled downward digit by the divisor. Thus, the side by side step is to separate 35 by 4. The consequence is "8", so add together "8" to the quotient.
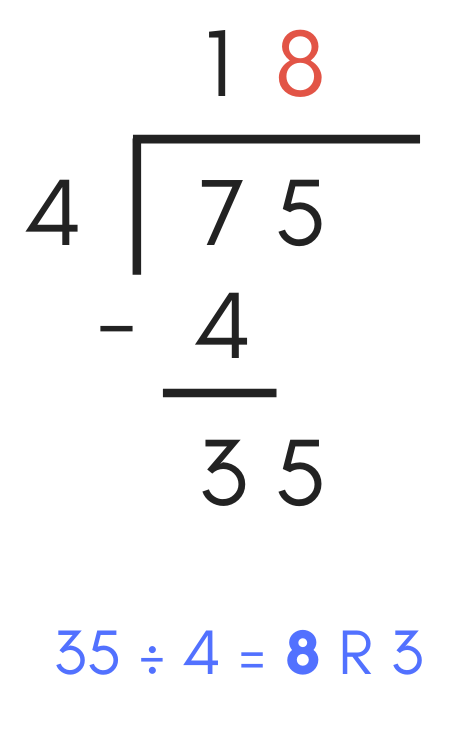
Next, multiply the caliber digit "8" by the divisor "4", which equals 32. Add "32" to the long sectionalisation problem.
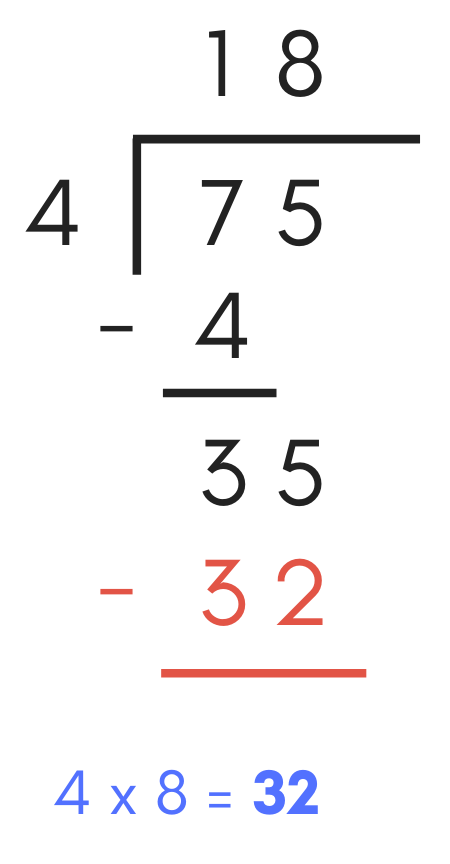
Next, repeat the subtraction procedure, subtracting 32 from 35, which equals 3. Add a "3" below the subtraction line. Since there are no longer any remaining digits in the dividend, this is the residual portion of the solution.
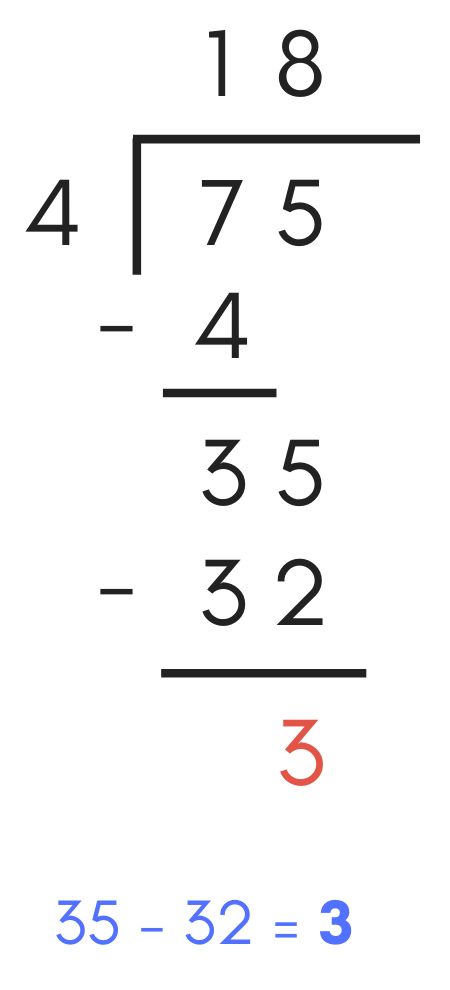
As you practise these steps, use the calculator above to ostend your answer and validate your steps solving long division issues.
How to get the Quotient and Remainder as a Decimal
If yous've gotten this far then you should have a skillful idea of how to calculate a long division problem, just y'all might be stuck if yous need to get the quotient as a decimal rather than a whole number with a residuum.
To calculate the quotient in decimal form, follow the steps above the get the whole number and remainder.
Side by side, divide the divisor by the remainder to become the residuum as a decimal. Finally, add the decimal to the caliber to go it in decimal class.
For example, 75 ÷ 4 is eighteen with a residual of iii.
Separate iii past iv to go the decimal 0.75.
three ÷ iv = 0.75
And then, add 0.75 to 18 to get the quotient as a decimal.
0.75 + 18 = 18.75
Thus, the decimal form of 75 ÷ 4 is 18.75.
randolphwifforge53.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.inchcalculator.com/long-division-calculator/
0 Response to "Division Calculator When You Know the Answer"
Post a Comment